Mitosis is a process of nuclear division in eukaryotic cells that occurs when a parent cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells. During cell division, mitosis refers specifically to the separation of the duplicated genetic material carried in the nucleus. Mitosis is conventionally divided into five stages known as prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. While mitosis is taking place, there is no cell growth and all of the cellular energy is focused on cell division.
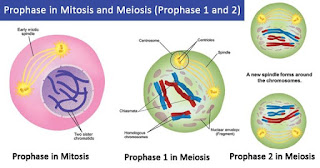
During prophase, the replicated pairs of chromosomes condense and compact themselves. The pairs of chromosomes that have been replicated are called sister chromatids, and they remain joined at a central point called the centromere. A large structure called the mitotic spindle also forms from long proteins called microtubules on each side, or pole, of the cell.
During prometaphase, the nuclear envelope that encloses the nucleus breaks down, and the nucleus is no longer separated from the cytoplasm. Protein formations called kinetochores form around the centromere. The mitotic spindle extends from the poles and attaches to the kinetochores.
During metaphase, the microtubules pull the sister chromatids back and forth until they align in a plane, called the equatorial plane, along the center of the cell.
During anaphase, the sister chromatids are separated simultaneously at their centromeres. The separated chromosomes are then pulled by the spindle to opposite poles of the cell. Anaphase ensures that each daughter cell receives an identical set of chromosomes.
Finally, during telophase, a nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes to separate the nuclear DNA from the cytoplasm. The chromosomes begin to uncoil, which makes them diffuse and less compact. Along with telophase, the cell undergoes a separate process called cytokinesis that divides the cytoplasm of the parental cell into two daughter cells.
Mitosis is an important part of cell division. In this stage the chromosome number of mother cell is similar in daughter cell. So, this stage is called 'Equational Cell Division'.